There are 12 main verb tenses in English and each serves a distinct purpose. This is a general overview on how the different tenses are used in writing.
Past Tenses
Past Simple
Used for completed past actions. Regular verbs take the “–ed” stem.
I studied yesterday.
Past Continuous/Progressive
Used for actions that happen for extended period of time in the past or when one past action interrupts another. It is formed using was/were + ing form of another verb.
I was studying when the phone rang.
Past Perfect
Used to indicate an event preceded another past event. This tense is formed using had + third form of a verb.
I had studied Business models before enrolling in the Commerce program at SMU.
Past Perfect Continuous
Used for an event that took place over an extended period of time in the past and then stopped in the past.
I had been studying Business models for two hours. when you arrived.
Present Tenses
Present Simple
Used for schedules, routines, and habits. It is formed with the first form of the verb. Note that most third person present simple verbs take an ‘s’
I write
She writes
Eric reviews his lecture notes daily.
Present Continuous/Progressive
Used for actions that are happen in this exact moment. It is formed using am/is/are + -ing form of another verb. If there is a time indicator, it can sometimes be used for the future.
I am creating this handout. (right now)
I am reviewing this handout tomorrow. (future as it has the time indicator tomorrow)
Eric is reviewing his lecture notes in the Atrium.
Present Perfect
Used for actions that happened at an unspecific time before the present and to talk about experiences. The time must be unspecific for this tense to be used.
Eric has reviewed his lecture notes.
Present Perfect Continuous
Used for something that started in the past but continued until the present. It is formed using have been + ing form of the verb.
I have been working here for three years.
Eric has been reviewing her lecture notes for 3 days.
Future Tenses
Future Simple
Has two forms will and going to that have specific uses. There are some exceptions to these rules:
Will is used for promises and voluntary actions
Going to is used for plans
Sarah will be an engineer.
Future Continuous/Progressive
Used when an action takes places in the future but it is interrupted. It is formed using will be + -ing form or going to + -ing form of a verb.
Jake will be studying sociology tonight before Shannon gets there.
Sarah will be working as an engineer next summer.
Future Perfect
Indicates an action that will be completed by a particular time in the future. It usually contains a time indicator. It is formed using will + have + past participle
She will have completed her degree by May 2015.
Sarah will have worked as an engineer for 4 years.
Future Perfect Continuous/Progressive
Used to describe an event that will take place and end at a particular moment in the future. It is formed using will have been + ing form or going to + have been + ing form of the verb.
Jane will have been working as a tutor for four years by 2016.
Sarah will have been working for 4 years by 2019.
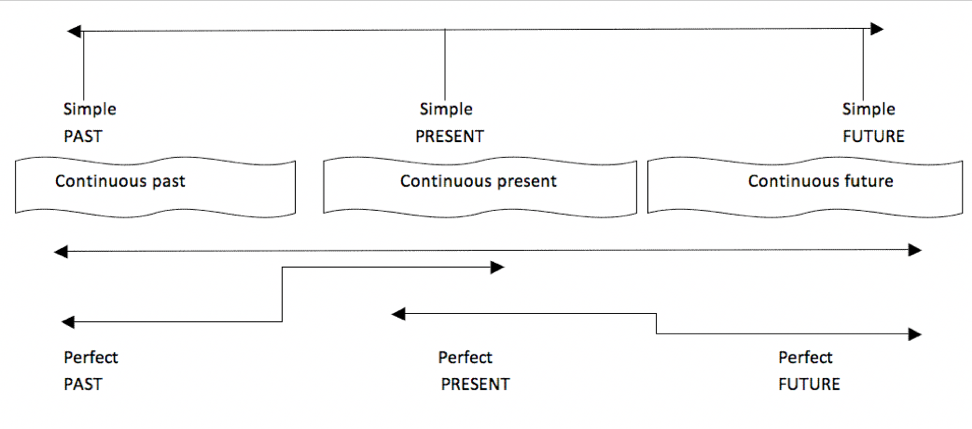
Timeline of Tenses
From: http://www.pics-searcher.appspot.com/?image=tenses-in-english-grammar-chart
Image description: Image shows timeline with single points for ‘simple past’, ‘simple present’, and ‘simple future’, at the beginning, middle, and end, respectively. Continuous past, continuous present, and continuous future are shown as bands overlapping with each of their respective paired simple tenses. Perfect past tense is shown as an arrow overlapping with both simple past and simple present, indicating its use in communicating order of past events. Perfect present and perfect future are represented by one line reaching from the centre to the end of the timeline with a break in the middle, indicating the continuity and ambiguity of time for perfect present, with a particular time indicated (end of timeline) for perfect future.
Practice ↓
Identify the correct verb tense(s) in the following sentences.
- I have been to China three times.
- I had been thinking about getting a cat when a stray appeared at my door.
- Carson was trying to fix the car.
- We will have seen five waterfalls by the end of the day.
- Although after graduation I will have been studying for 12 years, it is unclear to me what career I will pursue.
- Many scientists and theorists have argued that extra-terrestrial life is a distinct possibility.
- That noise is starting to get on my nerves.
- Michelle had thought there would be cake at the party.
- This summer I will be spending many days at the beach.
- I have been finding it difficult to take effective notes in online classes.
Answers ↓
- Present perfect
- Past perfect continuous; past simple
- Past continuous
- Future perfect
- Future perfect continuous; present simple; future simple
- Present perfect; present simple
- Present continuous
- Past perfect
- Future continuous
- Present perfect continuous