Introduction to Microsoft Excel
Get Started
Create a workbook
-
Open Excel

- Select Blank workbook or press Ctrl+N.
- Start typing.
Create a workbook from a template
- Select File > New.
- Double-click a template.
- Click and start typing.
Change Font, Style, Size, Colour, or Apply Effects
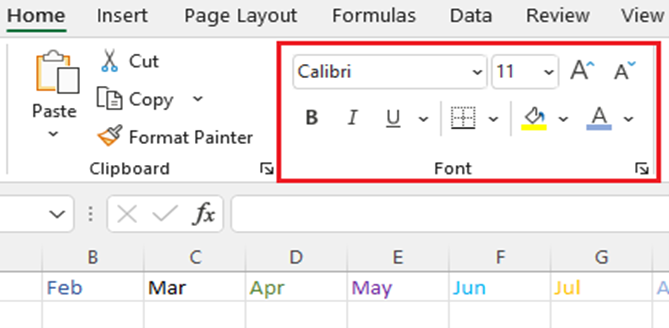
- Click Home and:
- For a different font style, click the arrow next to the default font Calibri and pick the style you want.
- To increase or decrease the font size, click the arrow next to the default size 11 and pick another text size
-
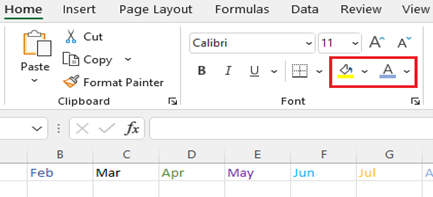
To change the font color, click Font Color and pick a color.
- To add a background color, click Fill Color next to Font Color.
-
To apply strikethrough, superscript, or subscript formatting, click the Dialog Box Launcher, and select an option under Effects.
Change the text alignment
- You can position the text within a cell so that it is centered, aligned left or right. If it’s a long line of text, you can apply Wrap Text so that all the text is visible.
- Select the text that you want to align, and on the Home tab, pick the alignment option you want.
Clear formatting
- If you change your mind after applying any formatting, to undo it, select the text, and on the Home tab, click Clear > Clear Formats.
Cleaning Data
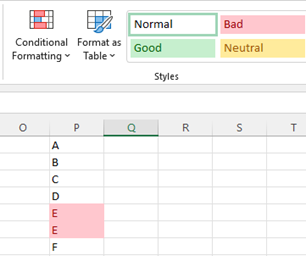
To remove duplicate values,
- Click Data > Data Tools > Remove Duplicates.
To highlight unique or duplicate values
- Use the Conditional Formatting command in the Style group on the Home tab.
-
Select Highlight Cells Rules > Duplicate Values
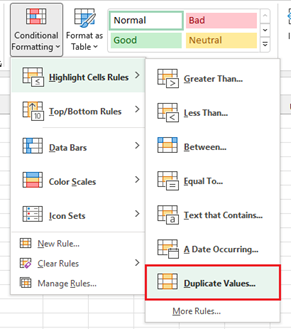
- Any duplicates in the selected range will then be highlighted
The Transpose feature:
- Select the range of data you want to rearrange, including any row or column labels, and either select Copy Copy icon on the Home tab, or press CONTROL+C.
-
Select the first cell where you want to paste the data, and on the Home tab, click the arrow next to Paste, and then click Transpose.
- Pick a spot in the worksheet that has enough room to paste your data. The data you copied will overwrite any data that’s already there.
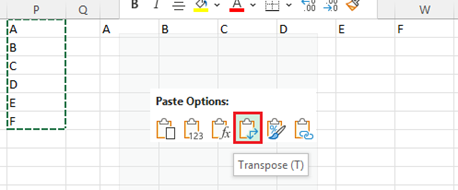
- After rotating the data successfully, you can delete the original data.
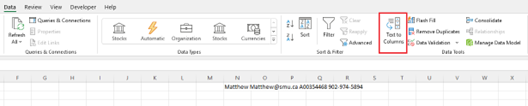
Delimiters:
- Select the cell or column that contains the text you want to split.
-
Select Data and under Data Tools, select Text to Columns.
-
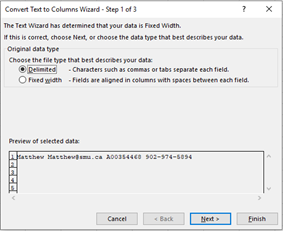
In the Convert Text to Columns Wizard, select Delimited > Next.
-
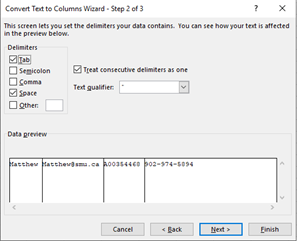
Select the Delimiters for your data. For example, Comma and Space. You can see a preview of your data in the Data preview
- Select Next.
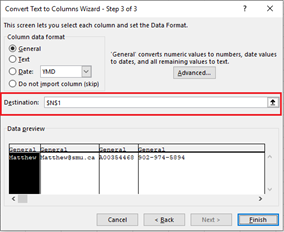
-
Select the Destination in your worksheet which is where you want the split data to appear.
-
Select Finish.
Process Data
Turning your data into a table
- Select the cells that contain the information for the table.
-
Click the Insert tab > Locate the "Tables" group.
-
Click Table.
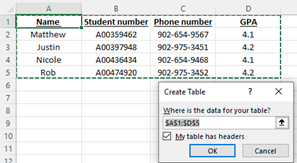
- A "Create Table" dialog box will open.
- If you have column headings, check the box My table has headers.
-
Verify that the range is correct > Click OK.
-
Resize your columns to make the headings visible.
AutoFill Sequences
-
Select one or more cells you want to use as a basis for filling additional cells.
- For a series like 1, 2, 3, 4, 5..., type 1 and 2 in the first two cells. For the series 2, 4, 6, 8..., type 2 and 4.
- For the series 2, 2, 2, 2..., type 2 in first cell only.
-
Drag the fill handle Fill handle.

-
If needed, click Auto Fill Options Button
 and choose the option you want.
and choose the option you want.
- And the series is filled in for you automatically using the AutoFill feature.
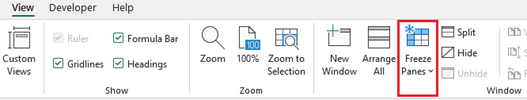
Freeze the first column
- Select View > Freeze Panes > Freeze First Column.
Freeze the first two columns
- Select the third column.
- Select View > Freeze Panes > Freeze Panes.
Freeze columns and rows
- Select the cell below the rows and to the right of the columns you want to keep visible when you scroll.
-
Select View > Freeze Panes > Freeze Panes.
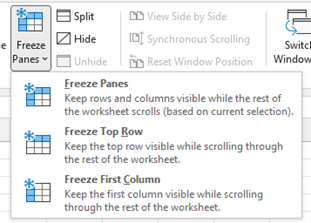
Unfreeze rows or columns
-
On the View tab > Window > Unfreeze Panes.
How to insert one or more rows/columns.
- Select the row below where you want the new rows to appear.
-
Right click on the highlighted row and select "Insert" from the list. This will insert one row above the row you initially highlighted.
-
Add multiple rows or columns, highlight the same number of pre-existing rows or columns that you want to add. Then, right-click and select Insert.
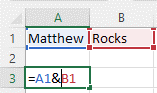
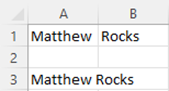
Combine Text from Multiple Cells
- Select the cell in which you want the combined data
- Type an = (equal sign) to start the formula
- Click on the first cell
- Type the & operator (shift + 7)
- Click on the second cell
-
Press Enter to complete the formula
Analyze Data
Adding a Filter
- Select any cell within the range.
-
Select Data > Filter.
- Select the column header arrow Filter arrow.
- Select Text Filters or Number Filters, and then select a comparison, such as Between.
- Enter the filter criteria and select OK.
Filter data in a table
- When you Create and format tables, filter controls are automatically added to the table headers.
-
Select the column header arrow Filter drop-down arrow for the column you want to filter.
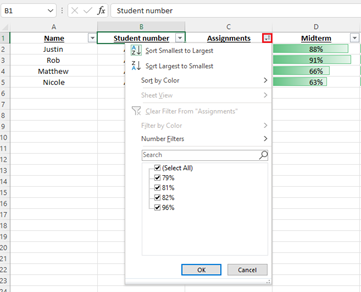
-
Uncheck (Select All) and select the boxes you want to show.
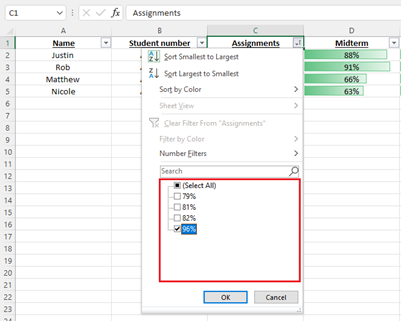
- Click OK.
-
The column header arrow Filter drop-down arrow changes to a Applied filter icon Filter icon. Select this icon to change or clear the filter.
Conditional Formatting
- Select the table or range where you want to change the background color of cells
-
Navigate to the Home tab, under Styles group, choose Conditional Formatting > New Rule….
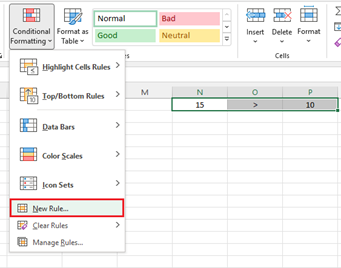
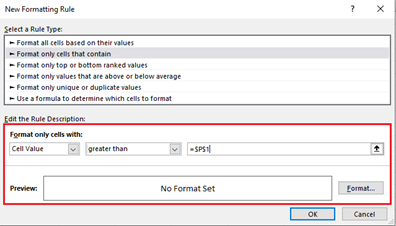
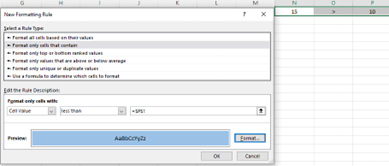
- In the New Formatting Rule dialog box, select "Format only cells that contain" under "Select a Rule Type" box.
-
In the lower part of the dialog box under "Format Only Cells with section", set the rule conditions
- Click the Format
-
In the Format Cells dialog box, switch to the Fill tab and select the color of your choice
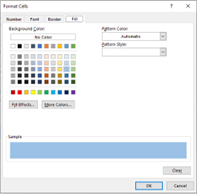
-
Click OK.
-
Back on the New Formatting Rule window, click OK
Equal sign:
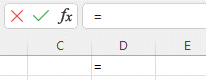
- Before creating any formula, you’ll need to write an equal sign (=) in the cell where you want the result to appear.
Addition:
- To add the values of two or more cells, use the + sign. Example: =C1+D4.
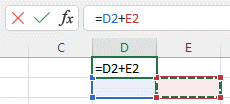
Subtraction:
- To subtract the values of two or more cells, use the - sign. Example: =C1-D4.
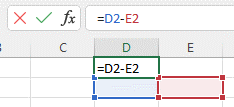
Multiplication:
- To multiply the values of two or more cells, use the * sign. Example: =C1*D4.
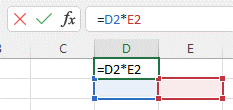
Division:
- To divide the values of two or more cells, use the / sign. Example: =C1/D4.
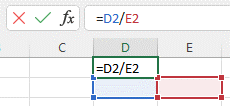
Example: =(C1 - D4) / ((A5 + B6) * 3).
SUM:
- The SUM function automatically adds up a range of cells or numbers. To complete a sum, you would input the starting cell and the final cell with a colon in between. Here’s what that looks like: SUM(Cell1:Cell2).
Example: =SUM(C5:C30).
AVERAGE:
- The AVERAGE function averages out the values of a range of cells. The syntax is the same as the SUM function: AVERAGE(Cell1:Cell2). Example: =AVERAGE(C5:C30).
IF:
- The IF function allows you to return values based on a logical test. The syntax is as follows: IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false]). Example: =IF(A2>B2,"Over Budget","OK").
VLOOKUP:
- The VLOOKUP function helps you search for anything on your sheet’s rows. The syntax is: VLOOKUP(lookup value, table array, column number, Approximate match (TRUE) or Exact match (FALSE)).
Example: =VLOOKUP([@Attorney],tbl_Attorneys,4,FALSE).
INDEX:
- The INDEX function returns a value from within a range. The syntax is as follows: INDEX(array, row_num, [column_num]).
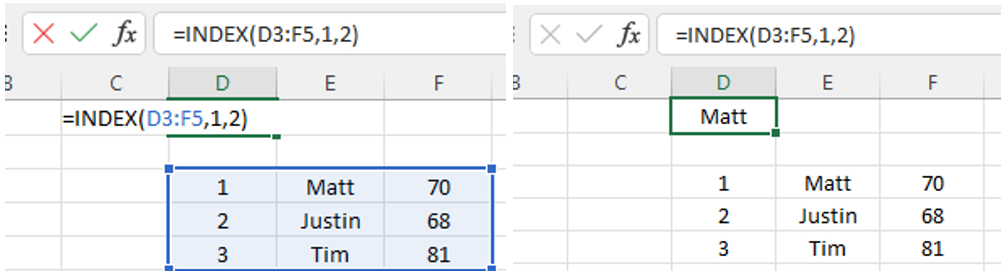
MATCH:
- The MATCH function looks for a certain item in a range of cells and returns the position of that item. It can be used in tandem with the INDEX function. The syntax is: MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, match_type]).
COUNTIF:
- The COUNTIF function returns the number of cells that meet a certain criteria or have a certain value. The syntax is: COUNTIF(range, criteria). Example: =COUNTIF(A2:A5,"London").
Absolute Reference
- The dollar sign ($) fixes the reference to a given cell, so that it remains unchanged no matter where the formula moves. In other words, using $ in cell references allows you to copy the formula in Excel without changing references.
Switch between absolute, relative, and mixed references (F4 key).
- Select the cell you wish to edit.
- Enter Edit mode by pressing the F2 key or double-click the cell.
-
Select the cell reference you want to change.
- Press F4 to toggle between four cell reference types.
Create a PivotTable:
-
Select Insert > PivotTable.
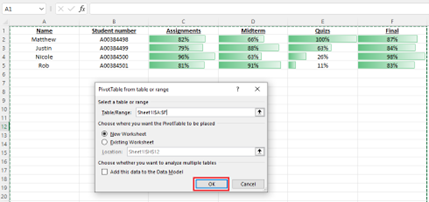
- Under Select a table or range, In the Table/Range field, select the desired data for your chart.
-
Under Choose where you want the PivotTable report to be placed
- Select New worksheet to place the PivotTable in a new worksheet or
- Select Existing worksheet and then select the location you want the PivotTable to appear.
-
Select OK.
PivotTable Fields:
- After you click OK on the PivotTable from the table or range you will be presented with options to add PivotTable Fields.
-
The Field List has a field section in which you pick the fields you want to show in your PivotTable.
- If you click inside the PivotTable but don't see the Field List, open it by clicking anywhere in the PivotTable. Then, select the PivotTable Analyze on the ribbon.
-
Click Field List.
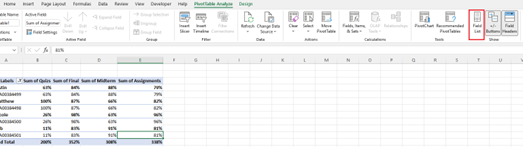
PivotTable Options:
- Report Filter: This allows you to only look at certain rows in your dataset.
- Column Labels: These would be your headers in the dataset.
- Row Labels: These could be your rows in the dataset. Both Row and Column labels can contain data from your
- Value: This section allows you to look at your data differently. Instead of just pulling in any numeric value, you can sum, count, average, max, min, count numbers, or do a few other manipulations with your data. In fact, by default, when you drag a field to Value, it always does a count.
Data Validation
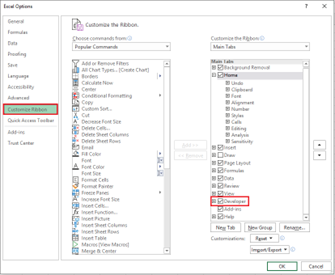
Developer Tag
-
Click File > Options > Customize Ribbon, select the Developer check box, and click OK.
Adding a Checkbox
-
To add a check box, click the Developer tab, click Insert, and under Form Controls, select the checkbox option.
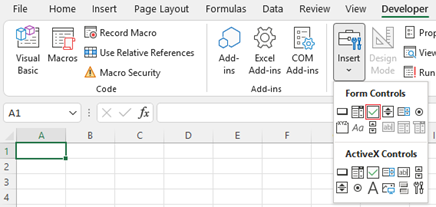
- Click in the cell where you want to add the check box or option button control.
- To edit or remove the default text for a control, click the control, and then update the text as needed.
Inserting a Hyperlink
- Press Shift K.
-
From there a box will pop up allowing you to place the hyperlink URL.
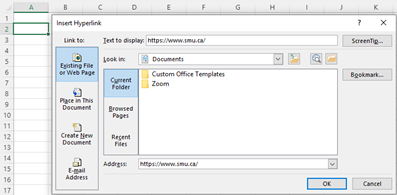
-
Copy and paste the URL into this box and hit OK or click Enter.
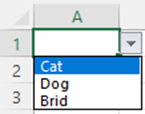
Data Validation
- Highlight the cells you want the drop-downs to be in
- Then click the Data menu in the top navigation
-
Under the Data Tools menu, click Data Validation.
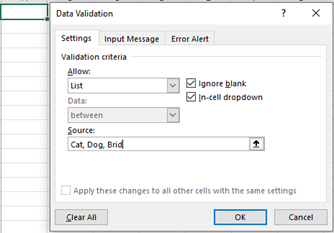
- From there, you'll see a Data Validation Settings box
- Under the Allow options, click Lists.
- Check the In-Cell dropdown button.
-
Under Source you can enter data separated by a comma or select and highlight a field of cells that your drop-down menu will reference.
-
Press OK.